Bienvenue sur notre site
Ceci est un exemple de contenu de page. Adaptez ce contenu selon vos besoins.
Ceci est un exemple de contenu de page. Adaptez ce contenu selon vos besoins.
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is a pivotal regulation by the European Commission aimed at bolstering the digital operational resilience of the financial sector. Enacted to address the evolving digital risks and ensure financial institutions can effectively withstand, respond to, and recover from ICT-related disruptions, DORA introduces a comprehensive regulatory framework. Its main objectives include improving ICT risk management, enhancing cybersecurity measures, establishing robust governance and oversight, and promoting effective incident reporting and business continuity planning among financial entities operating within the EU.
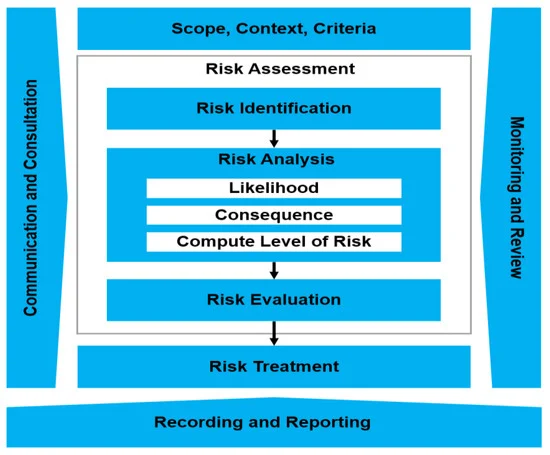
In the context of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), financial institutions are encouraged to adopt comprehensive ICT Risk Management practices. While DORA provides a regulatory framework for digital operational resilience, institutions may refer to various established standards to enhance their ICT risk management capabilities:
Adhering to these frameworks can significantly enhance an institution's resilience against ICT-related risks, aligning with DORA's objectives to strengthen the digital operational resilience across the EU's financial sector.
Mapping of IT Assets :
Compile a comprehensive inventory of systems, applications, databases, and digital infrastructure. This includes both internally hosted assets and cloud services.
Identification of Critical Assets :
Determine the essential business processes and the IT systems that support them. This may include transaction processing systems, customer databases, CRM applications, and other key systems.
Identify Risks :
Systematically identify and document all potential risks that could impact ICT systems and operations.
Risk Analysis :
Assess potential threats such as cyber attacks, technical failures, human errors, and natural disasters. This should involve an analysis of the likelihood and impact of each risk scenario.
Business Impact Assessment (BIA) :
For each critical asset, evaluate the potential impact of a disruption on banking operations. This aids in prioritizing resilience efforts based on the significance of each asset to daily operations.
Evaluate and Prioritize Risks :
Evaluate the risks to prioritize them based on their severity and the urgency of mitigation actions required.
Defining the Level of Risk Appetite :
In collaboration with key stakeholders, establish the acceptable level of risk for each business process and IT system. This will guide decisions regarding investments in security and resilience.
Evaluate and Prioritize Risks :
Evaluate the risks to prioritize them based on their severity and the urgency of mitigation actions required.
Implement Mitigation Strategies :
Develop and implement appropriate strategies to mitigate the prioritized risks, including preventive measures and contingency plans.
Monitor and Review :
Continuously monitor the risk environment and the effectiveness of implemented mitigation strategies, adjusting as necessary to address new or changing risks.
Enhance ICT Resilience :
Strengthen the resilience of ICT systems against disruptions through robust design, redundancy, and recovery planning.
Compliance with Regulations :
Ensure compliance with all relevant legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations related to ICT risk management.
Stakeholder Communication :
Maintain open and effective communication with all stakeholders regarding ICT risks and the measures taken to manage them.
The "Risk Analysis Report" serves to systematically identify, assess, and prioritize risks to the financial entity’s operations, particularly focusing on the identification of critical assets as mandated by the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). This comprehensive document aims to inform strategic decision-making and guide the development of effective risk mitigation strategies.
The report encompasses a broad range of potential risks, including cybersecurity threats, operational vulnerabilities, systemic failures, and external threats impacting the entity’s critical assets and functions. It provides a sector-wide perspective while also considering entity-specific risk factors.
Explanation of the methodologies and tools used in conducting the risk analysis, including data sources, assessment frameworks, and analytical techniques.
Concluding remarks summarizing the key findings of the risk analysis, highlighting priority risks, and proposing strategic recommendations for enhancing the entity’s operational resilience.
By leveraging the insights provided in the "Risk Analysis Report," financial entities can adopt a proactive and informed approach to managing risks, ensuring the protection of critical assets and compliance with DORA’s requirements for operational resilience.
The "Critical Assets Identification Plan" outlines a structured approach for identifying and prioritizing the assets that are essential to the financial entity's operations and resilience. In alignment with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), this plan aims to ensure that financial entities can accurately identify, assess, and protect their critical assets against various risks and vulnerabilities.
This plan covers the processes and criteria for identifying critical assets across the entity, including information systems, data repositories, operational technologies, and essential personnel. It focuses on assets that, if compromised, could significantly impact the entity's operational capability, reputation, or regulatory compliance.
Details on the phased implementation of the critical assets identification plan, including timelines, milestones, and resource allocation.
Considerations for ensuring that the critical asset identification process aligns with DORA regulations and other relevant standards, including mechanisms for reporting and documentation.
By adopting the "Critical Assets Identification Plan," financial entities can systematically identify and protect their critical assets, enhancing their operational resilience in compliance with DORA's requirements.
The "Risk Appetite Framework" is designed to articulate the level of risk a financial entity is willing to accept in pursuit of its strategic objectives, in alignment with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). This framework establishes clear guidelines for risk decision-making, ensuring that all activities are conducted within acceptable risk thresholds to safeguard the entity's operational resilience.
This document encompasses the entire spectrum of risks faced by the entity, including but not limited to cybersecurity threats, operational disruptions, and compliance risks. It covers the processes for identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring risks across the entity's operations.
A detailed plan for implementing the risk appetite framework, including timelines, milestones, and responsibilities for key activities.
Discussion on the benefits of implementing a risk appetite framework, including enhanced decision-making, improved resource allocation, and strengthened operational resilience.
By establishing a "Risk Appetite Framework," financial entities can systematically manage their risk exposures, making informed decisions that balance opportunity and risk, in compliance with DORA's emphasis on operational resilience.
In those interconnected world, cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to individuals, organizations, and nations. The DORA Resilience Act recognizes the critical importance of information sharing in combating these threats. This chapter focuses on the principles, mechanisms, and benefits of cybersecurity information sharing as outlined in the DORA Resilience Act.
Effective cybersecurity information sharing enables stakeholders to proactively detect, prevent, and respond to cyber incidents. By exchanging threat intelligence, best practices, and vulnerabilities, entities can enhance their collective defenses and resilience against cyber threats.
Throughout this chapter, we will explore key aspects of cybersecurity information sharing, including its role in fostering collaboration among public and private sector entities, ensuring privacy and data protection, and promoting trust and transparency.
Use the TIBER-EU framework to guide resilience testing. Organize teams for penetration testing and red team attack simulations in collaboration with external partners.
Identify and prioritize systems and processes for resilience testing based on their criticality to business operations.
Develop testing scenarios that reflect potential disruptions, including cyber attacks, system failures, and disaster response.
Plan tests that challenge the organization's ability to respond and recover from disruptions while minimizing impact to operations.
This document outlines a structured approach to resilience testing for financial entities, aimed at assessing and enhancing their ability to withstand and recover from cyber threats, technical failures, and other disruptions. The framework is designed to ensure comprehensive testing coverage across all critical IT systems and processes, aligning with DORA's emphasis on maintaining digital operational resilience in the financial sector.
The Resilience Testing Framework applies to all operational and information systems, including networks, applications, and services critical to the daily functions of financial entities. It encompasses various testing methodologies, such as vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, scenario-based simulations, and disaster recovery exercises.
Offers detailed guidance for implementing the testing framework, including prerequisites, tools and resources, stakeholder communication, and coordination with external partners or service providers.
Ensures that the resilience testing practices comply with relevant regulations and standards, and supports the organization's efforts to meet DORA's requirements for digital operational resilience.
Establishes a structured review process for regularly updating the testing framework to adapt to evolving threats, technological changes, and regulatory developments.
The Resilience Testing Framework Document serves as a foundational tool for financial entities to systematically assess and enhance their digital operational resilience, supporting their ongoing compliance with DORA's objectives and ensuring the stability of the financial system.
This document provides a comprehensive guide on the various testing scenarios and methodologies that financial entities should employ to assess their digital operational resilience. It aims to ensure that entities can effectively identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and ensure continuity of operations in the face of cyber threats and other disruptions, in line with the requirements set forth by DORA.
The scope includes a wide array of testing scenarios and methodologies ranging from technical vulnerability assessments to complex business continuity and disaster recovery exercises. It covers both cyber and physical aspects of operational resilience, encompassing IT systems, network infrastructure, applications, and critical business processes.
Provides detailed guidance on implementing the testing scenarios and methodologies, including planning, resource allocation, stakeholder engagement, and coordination with third-party service providers.
Details the requirements for documenting testing processes, findings, and remediation actions. It also outlines reporting protocols to ensure that relevant insights are communicated to management, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders.
Establishes mechanisms for the continuous review and enhancement of testing scenarios and methodologies based on evolving threats, technological advancements, and lessons learned from previous tests.
By adhering to the outlined Testing Scenarios and Methodologies, financial entities can strengthen their digital operational resilience, ensuring they are prepared to manage and recover from disruptions in accordance with DORA's objectives.
The "Test Planning and Scheduling Timeline" document aims to provide a structured and strategic approach to planning, executing, and reviewing digital operational resilience tests. This timeline ensures that financial entities systematically address all aspects of digital resilience, including cybersecurity, data integrity, and business continuity, as mandated by the DORA regulations.
The timeline covers all phases of the testing process for digital operational resilience, from initial planning to post-test review. It encompasses various testing types such as vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and business continuity exercises, ensuring comprehensive resilience across all digital operations.
Emphasizes the integration of test outcomes with the entity’s overall risk management framework, enhancing the entity’s resilience posture and compliance with DORA regulations.
Highlights the importance of updating the testing timeline based on test results, evolving threats, and changes in the regulatory landscape, ensuring ongoing resilience and compliance.
By adhering to the "Test Planning and Scheduling Timeline," financial entities can ensure that their digital operational resilience testing is comprehensive, strategic, and aligned with the objectives of the DORA framework, thereby enhancing their overall resilience and regulatory compliance.
Carry out planned tests, simulating various disruption scenarios to evaluate the effectiveness of response plans.
Engage both internal teams and external partners to ensure comprehensive testing across all critical functions.
Document test results, including any identified weaknesses or failures in existing resilience strategies.
The "Detailed Report of Test Outcomes" document is designed to provide a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the outcomes from digital operational resilience tests. This report aims to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in the entity's digital operational resilience, in accordance with the DORA framework.
The report covers the outcomes of various resilience tests, including but not limited to cybersecurity penetration tests, vulnerability assessments, and business continuity and disaster recovery exercises. It evaluates the effectiveness of the entity’s defenses against potential disruptions and cyber threats.
Ensures that the report meets the reporting requirements set forth by DORA, facilitating regulatory compliance and supporting transparent communication with supervisory authorities.
The "Detailed Report of Test Outcomes" serves as a critical tool for financial entities to assess and enhance their digital operational resilience, providing actionable insights to address vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses in line with DORA's objectives.
This document provides an in-depth analysis of the effectiveness of an entity's response mechanisms to simulated disruptions and cyber threats encountered during resilience testing. The goal is to evaluate the robustness and efficiency of existing response strategies and incident management processes, aligning with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) mandates.
The scope encompasses the assessment of response strategies across a variety of test scenarios, including cybersecurity incidents, data breaches, system failures, and physical disruptions. It aims to cover all critical aspects of the entity's operational resilience, from technical response capabilities to communication and coordination efforts.
Describes the methodologies and criteria used to evaluate response effectiveness, including qualitative assessments, quantitative metrics, and benchmarking against industry best practices.
By conducting a thorough "Analysis of Response Effectiveness," financial entities can gain valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of their response strategies, driving continuous improvement and ensuring compliance with DORA's operational resilience requirements.
This document aims to provide actionable recommendations for enhancing the digital operational resilience of financial entities based on the outcomes of resilience testing. It focuses on identifying areas of improvement to mitigate vulnerabilities, strengthen defenses, and optimize incident response mechanisms, aligning with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The recommendations cover a broad spectrum of resilience aspects, including cybersecurity, data protection, system availability, and business continuity. They are derived from a comprehensive analysis of test results, including vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and business impact analyses.
Provides a roadmap for implementing the recommendations, including prioritization based on risk assessment, resource allocation, and timelines for execution.
By following these "Recommendations for Improvements Based on Test Results," financial entities can systematically address the findings from resilience tests, significantly enhancing their digital operational resilience in compliance with DORA's requirements.
Analyze test results to identify and understand the root causes of any failures or shortcomings in operational resilience.
Update and enhance resilience plans and strategies based on test findings and identified areas for improvement.
Implement changes and conduct follow-up tests to ensure that enhancements effectively strengthen operational resilience.
Adoption of Metasploit for penetration tests and Cyber Range for attack simulations.
Post-test analyses to identify and correct vulnerabilities.
This document outlines the updated operational resilience plans formulated in response to the findings from recent resilience testing and assessments. It aims to enhance the financial entity's preparedness against a wide range of potential disruptions, ensuring compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and bolstering the entity’s overall operational resilience.
The revised plans encompass improvements across all facets of operational resilience, including but not limited to cybersecurity defenses, data integrity protocols, business continuity strategies, and incident response mechanisms. The scope extends to all operational areas that could impact the financial entity's ability to deliver critical services.
Details the approach for implementing the revised operational resilience plans, including timelines, responsibilities, resource allocation, and monitoring mechanisms to track progress and effectiveness.
Establishes an ongoing process for regularly reviewing and updating the operational resilience plans based on evolving threats, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, ensuring sustained resilience and compliance.
By adopting the "Revised Operational Resilience Plans," financial entities can significantly enhance their capability to withstand and recover from operational disruptions, thereby ensuring the stability and integrity of their services in alignment with DORA's objectives.
The aim of this document is to outline the enhancements made to the entity's response strategies and procedures following a comprehensive review of existing measures and recent resilience test outcomes. These updates are designed to bolster the entity's capability to effectively respond to and recover from operational disruptions, in line with the mandates of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
This document encompasses revised strategies and procedures across various response domains, including cybersecurity incident response, data breach management, system failure recovery, and physical security breaches. It aims to cover all critical aspects necessary for maintaining operational continuity and protecting against potential threats.
Details the implementation plan for the updated response strategies and procedures, including timelines, responsible parties, and monitoring mechanisms to assess effectiveness and identify areas for further improvement.
Ensures that the updated response strategies and procedures align with current regulatory requirements and best practices, maintaining compliance with DORA and other relevant standards.
By implementing the "Updated Response Strategies and Procedures," financial entities can strengthen their resilience against operational disruptions, ensuring robust and efficient response capabilities in alignment with the objectives of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The objective of this document is to present the outcomes of follow-up resilience tests conducted after the initial implementation of updated resilience measures. It aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of the financial entity's operational resilience against the backdrop of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), highlighting areas of success and pinpointing remaining vulnerabilities.
This assessment covers the range of follow-up tests performed, including but not limited to, cybersecurity penetration tests, business continuity simulations, and disaster recovery exercises. It evaluates the entity’s enhanced defenses, response strategies, and recovery capabilities in the face of potential operational disruptions.
Outlines the approach for implementing the final recommendations, including monitoring strategies to ensure continuous improvement in operational resilience.
Ensures that the entity’s operational resilience testing and assessment practices are in compliance with DORA requirements, including necessary reporting to regulatory bodies.
The "Follow-up Test Results and Final Resilience Assessment" document serves as a critical tool for financial entities to validate the effectiveness of their resilience enhancements and to plan for ongoing improvements in alignment with DORA's objectives for digital operational resilience.
As digital technologies become increasingly integral to business operations, the need for robust ICT Incident Management and Cyber Threat Reporting mechanisms has never been more critical. These processes are essential for detecting, responding to, and mitigating the impacts of cybersecurity incidents and threats. An effective incident management strategy ensures that an organization can swiftly address security breaches, minimize operational disruptions, and reduce the risk of data loss or theft. Additionally, systematic cyber threat reporting supports the early identification of potential threats and vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to strengthen their defenses against future attacks.
Develop an ICT incident response plan tailored to identify, manage, and mitigate incidents efficiently.
Implement detection systems and establish protocols for immediate incident reporting.
Train the incident response team on standard operating procedures and simulation exercises.
The "Incident Response Plan" is a comprehensive document that outlines the procedures and protocols a financial entity will follow in the event of an ICT security incident. This plan is developed to ensure a coordinated and effective response to incidents that could impact the entity's information and technology systems, in compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The plan covers the full spectrum of potential ICT incidents, including cybersecurity breaches, data leaks, system failures, and other events that could threaten the operational integrity or security of the entity's ICT environment.
Provisions for regular training and simulation exercises to ensure the incident response team and relevant personnel are prepared to execute the plan effectively.
Mechanisms for the ongoing review and updating of the incident response plan to adapt to new threats, technological changes, and regulatory requirements.
By establishing a robust "Incident Response Plan," financial entities can ensure a swift and effective response to ICT incidents, minimizing impact and enhancing resilience in line with DORA's objectives.
The "Threat Intelligence Reports" are designed to provide financial entities with detailed and actionable intelligence on emerging and evolving cyber threats. These reports are a critical component of an effective ICT incident management protocol, as mandated by the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), enabling entities to proactively identify, assess, and respond to potential threats to their ICT infrastructure and operations.
The reports cover a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, advanced persistent threats (APTs), insider threats, and vulnerabilities in hardware and software. They aim to provide a comprehensive view of the threat landscape, including tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries, as well as indicators of compromise (IoCs) that can aid in detection and response.
An outline of the methodologies used to gather and analyze threat intelligence, including sources of information, analytical tools, and collaboration with external cybersecurity organizations.
Guidelines for the secure distribution and access of the threat intelligence reports, ensuring that sensitive information is protected and only accessible to authorized personnel.
By regularly reviewing "Threat Intelligence Reports," financial entities can stay informed about the latest cyber threats, enhancing their preparedness and resilience in accordance with DORA's objectives for operational resilience and cybersecurity.
The "Incident Detection and Reporting Procedures" document establishes a structured approach for the timely detection, assessment, and reporting of ICT incidents within financial entities. In compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), these procedures are designed to ensure that potential and actual cybersecurity incidents are identified and communicated effectively, facilitating rapid response and mitigation efforts to protect the entity’s operational integrity.
The procedures apply to all types of ICT incidents that could affect the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the entity's data and systems. This includes, but is not limited to, cybersecurity breaches, data leaks, service outages, and system failures.
Details on training programs and awareness initiatives to ensure that all relevant personnel are familiar with the incident detection and reporting procedures, emphasizing the importance of prompt and accurate reporting.
Mechanisms for the regular review and updating of detection and reporting procedures to reflect changes in the threat landscape, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements.
By implementing the "Incident Detection and Reporting Procedures," financial entities can enhance their readiness to identify and respond to ICT incidents promptly, supporting their operational resilience in line with DORA's objectives.
The "Incident Analysis and Forensics" document outlines the methodologies and procedures for conducting thorough investigations into ICT incidents within financial entities. This critical component of ICT incident management protocols, as mandated by the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), aims to determine the root causes of incidents, assess their impact, and gather evidence for remedial actions and potential legal proceedings.
The scope of this document includes the analysis of cybersecurity breaches, system failures, data integrity issues, and any other ICT incidents that could compromise the operational resilience of the financial entity. It covers the entire process from the initial detection of an incident to the final reporting, including evidence preservation, analysis, and documentation.
Details on training programs for the incident response team, ensuring members are proficient in the latest forensic methodologies and tools.
Mechanisms for incorporating lessons learned from incident analyses into the entity’s cybersecurity practices and incident management protocols.
By establishing robust "Incident Analysis and Forensics" procedures, financial entities can effectively investigate ICT incidents, mitigate their impact, and enhance their preparedness for future cybersecurity challenges in alignment with DORA's guidelines.
The "Risk Management Framework" is a critical deliverable within the "Establishing ICT Incident Management Protocols" chapter under DORA. This framework outlines a comprehensive approach to identifying, assessing, managing, and mitigating ICT-related risks within financial entities. It serves as a guide to ensure the operational resilience of the financial sector against various ICT threats and vulnerabilities.
The "Risk Management Framework" is vital for establishing a proactive and structured approach to managing ICT risks. It enables financial entities to enhance their resilience, ensuring continuity of operations and protection of critical assets in the face of ICT incidents. By adhering to this framework, entities can also demonstrate compliance with DORA's requirements, contributing to the overall stability and security of the financial sector.
This document outlines the strategic approach to communicating with stakeholders during and after ICT incidents, in alignment with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). The plan ensures timely, accurate, and effective communication to maintain trust and transparency with clients, regulators, partners, and the public.
The objective of the "Stakeholder Communication Plan" is to establish predefined communication protocols to manage information dissemination during ICT incidents, minimizing misinformation and maintaining operational integrity.
The scope includes all internal and external stakeholders impacted by ICT incidents, detailing communication channels, messaging strategies, and escalation procedures.
Detailed strategy for implementing the communication plan, including training for spokespersons and simulation exercises.
By adhering to the "Stakeholder Communication Plan," financial entities can ensure that all parties are promptly and accurately informed during ICT incidents, fostering resilience and compliance with DORA's guidelines.
Educational initiatives aimed at bolstering the cybersecurity knowledge and practices of the workforce, thus minimizing the risk of human error-induced incidents.
Set up a system for internal reporting of cyber threats to designated officers within the organization.
Establish communication channels with external financial authorities and industry partners for threat intelligence sharing.
Create a database for documenting and analyzing reported cyber threats to enhance defensive strategies.
These guidelines aim to establish a consistent and effective framework for reporting cyber threats within financial entities, in accordance with DORA requirements. The goal is to enhance digital operational resilience by improving threat detection, information sharing, and incident response.
These guidelines apply to all financial entities regulated under DORA, including banks, insurance companies, asset managers, and payment service providers. They cover all types of cyber threats that could affect the continuity and integrity of financial services.
Assign clear responsibilities within the organization for reporting cyber threats, including the roles of management, IT staff, and information security personnel.
Implement training and awareness programs to ensure all staff understand their responsibilities in terms of reporting cyber threats.
Establish a schedule for regular review of the guidelines to adapt them to evolving cyber threats and regulatory requirements.
Adhering to these guidelines is crucial to the digital operational resilience strategy, ensuring a uniform and effective approach to managing and reporting cyber incidents. Compliance will help financial entities minimize the impacts of cyber incidents on their operations and the overall financial stability.
The purpose of these protocols is to establish standardized procedures for external communications related to cyber incidents, ensuring consistent, accurate, and timely information sharing with external stakeholders, including regulators, customers, and the public, in compliance with DORA requirements.
These protocols apply to all external communications following a cyber incident within financial entities regulated under DORA. This encompasses communications with regulatory bodies, customers, partners, media, and other external parties potentially affected by or interested in the incident.
Identify and utilize appropriate channels for different stakeholders, including press releases, social media, direct communications to customers, and regulatory filings.
Develop standardized templates for various types of incidents to ensure quick and consistent responses. Templates should be customizable to fit the specifics of each incident.
Define roles within the organization responsible for managing external communications during a cyber incident, including a primary spokesperson.
Conduct regular training for staff involved in external communications and perform drills to simulate the response to a cyber incident.
Regularly review and update the communication protocols to reflect changes in regulatory requirements, communication channels, and organizational structure.
Following these External Communication Protocols will help ensure that financial entities manage communications effectively in the wake of a cyber incident, maintaining transparency, trust, and compliance with regulatory expectations.
The Cyber Threat Database is designed to serve as a comprehensive repository for storing, categorizing, and analyzing information on cyber threats, vulnerabilities, incidents, and their countermeasures. Its purpose is to enhance the cybersecurity posture of financial entities by facilitating informed decision-making and proactive threat response, in alignment with DORA's emphasis on digital operational resilience.
This database covers a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, DDoS attacks, and other cyber-related security incidents that could potentially impact the operational resilience of financial entities regulated under DORA. It serves as a central resource for security analysts, IT professionals, and decision-makers within these organizations.
The database is accessible to authorized personnel within the organization, supporting collaboration across different departments to ensure a unified cybersecurity approach. It also enables controlled sharing of anonymized threat information with industry partners and regulatory bodies to foster a collective defense strategy.
Implements stringent data security and privacy measures to protect sensitive information contained within the database, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and industry standards.
Regularly updated to reflect the latest threat landscape, with continuous monitoring for new threats and vulnerabilities. Maintenance activities include data verification, quality control, and the integration of user feedback to enhance the database's utility and accuracy.
By maintaining a dynamic and comprehensive Cyber Threat Database, financial entities can significantly improve their ability to identify, assess, and respond to cyber threats, thereby reinforcing their resilience against cyber-attacks in line with DORA's objectives.
In today’s interconnected business environments, organizations increasingly rely on third-party ICT service providers to support critical operations and deliver key services. While these partnerships offer numerous benefits, including enhanced operational efficiency and access to specialized expertise, they also introduce a range of risks that must be carefully managed. ICT Service Provider Risk Management is a comprehensive approach designed to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor the risks associated with outsourcing ICT services. Effective risk management ensures that service provider engagements do not expose the organization to undue risk, safeguarding data integrity, operational resilience, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Create a comprehensive list of all ICT service providers, including cloud services, third-party support, and infrastructure providers.
Assess the criticality of each service provider in relation to the organization’s operational functions.
Establish criteria for evaluating the risk each service provider poses to the organization’s resilience.
Comprehensive evaluations of potential and existing service providers to identify and assess risks related to service delivery, data security, and compliance.
Regular audits and reviews of service provider operations to verify compliance with agreed-upon standards and regulatory requirements.
Development and implementation of strategies to reduce identified risks to acceptable levels, including contingency planning for critical service disruptions.
Establishment of communication and response protocols to ensure timely and coordinated action in the event of a security incident involving a service provider.
Robust procedures for managing contracts with ICT service providers, including regular reviews and renegotiations to address changing risk landscapes.
Conduct risk assessments for each ICT service provider based on the established criteria.
Identify and document any dependencies and potential single points of failure.
Evaluate the service providers’ own risk management and resilience measures.
The ICT Service Provider Risk Assessment Report aims to systematically evaluate the risks associated with leveraging external ICT service providers. This evaluation is critical to ensuring that financial entities maintain robust operational resilience in line with the mandates of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). The report identifies potential vulnerabilities and risk exposures from third-party engagements and proposes mitigation strategies to safeguard the entity’s digital operations.
The scope of this report includes a comprehensive assessment of all external ICT service providers engaged by the financial entity. It covers various dimensions of risk, including cybersecurity, data privacy, service availability, and compliance risks. The assessment extends to subcontractors and fourth parties where applicable, to ensure a complete view of the supply chain risk landscape.
Describes the methodology employed to conduct the risk assessment, including data sources, assessment criteria, and risk evaluation techniques.
Provides a summary of key findings and prioritized recommendations for enhancing the entity's management of ICT service provider risks, ensuring alignment with DORA's operational resilience objectives.
This "ICT Service Provider Risk Assessment Report" serves as an essential tool for financial entities to navigate the complexities of third-party risk management, ultimately strengthening their operational resilience in accordance with DORA regulations.
The objective of this document is to provide a detailed analysis of dependencies and single points of failure within the ICT service supply chain that could impact the operational resilience of financial entities. This analysis is essential for identifying vulnerabilities within the entity's operational infrastructure and for ensuring compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
This report encompasses an examination of all critical ICT services and components utilized by the financial entity, including both internal systems and external service providers. It aims to map out the interdependencies among these components and identify any single points of failure that could pose significant risks to the entity's operational continuity.
Overview of the methodologies used to conduct the analysis, including data collection techniques, risk evaluation methods, and tools for dependency mapping.
Summarizes the key findings of the analysis and emphasizes the importance of addressing identified dependencies and single points of failure to enhance the entity's operational resilience in accordance with DORA guidelines.
By conducting a thorough "Dependencies and Single Points of Failure Analysis," financial entities can proactively identify and mitigate risks within their ICT service supply chain, significantly enhancing their resilience and compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The "Service Provider Resilience Evaluation" document aims to assess the resilience of ICT service providers engaged by financial entities, ensuring these providers have robust mechanisms in place to maintain service continuity and protect against disruptions. This evaluation supports financial entities in complying with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) by ensuring their critical operations are supported by resilient ICT services.
This evaluation covers all external ICT service providers that supply critical services and infrastructure to the financial entity. It includes an assessment of their resilience in the face of cyber threats, technical failures, and other operational disruptions. The scope extends to the examination of service provider policies, procedures, and controls related to resilience and recovery capabilities.
Describes the methodologies used for conducting the resilience evaluation, including criteria for assessment, tools, and techniques for analysis, and approaches for engaging with service providers to gather necessary information.
Provides a summary of the evaluation findings, highlighting areas of strength and concern. It offers recommendations for the financial entity to address any identified gaps in service provider resilience, ensuring alignment with DORA requirements and enhancing overall operational resilience.
Conducting a "Service Provider Resilience Evaluation" is crucial for financial entities to understand and mitigate the risks associated with their reliance on external ICT services, ensuring compliance with DORA and strengthening their operational resilience framework.
Develop and implement risk management controls to mitigate identified risks associated with ICT service providers.
Establish service level agreements (SLAs) that include compliance with the organization’s security and resilience standards.
Set up continuous monitoring mechanisms to oversee service provider performance and adherence to SLAs.
Regular due diligence and auditing processes to ensure supplier compliance.
Contracts including clear security clauses and adequate service levels.
The "Risk Management Controls Framework" document is designed to establish a comprehensive set of controls and measures aimed at identifying, assessing, monitoring, and mitigating the various risks associated with ICT and digital operations within financial entities. This framework is developed to support entities in meeting the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) requirements, ensuring a robust defense against operational disruptions and cyber threats.
The framework covers the entire spectrum of ICT-related risks, including cybersecurity threats, data breaches, system failures, and third-party service provider vulnerabilities. It applies to all digital and ICT operations within the entity, spanning across internal systems, external services, and interconnected networks.
Detailed guidelines for the implementation of the risk management controls framework, including roles and responsibilities, timelines, and resource allocation.
Summarizes the importance of the risk management controls framework in enhancing the entity’s operational resilience, aligning with DORA’s objectives, and safeguarding against a broad range of digital and ICT risks.
By adopting the "Risk Management Controls Framework," financial entities can ensure a structured and effective approach to managing ICT and digital risks, supporting compliance with DORA and enhancing overall operational resilience.
The purpose of this document is to outline the establishment of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) between financial entities and their ICT service providers. These agreements are essential for defining the standards of service, performance metrics, and the responsibilities of both parties, ensuring that ICT services align with the operational resilience requirements set forth by the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The scope of these SLAs encompasses all ICT services procured by the financial entity, including cloud computing, data storage, cybersecurity solutions, and software applications. The agreements cover the delivery, management, and support of these services, focusing on the aspects critical to maintaining operational resilience.
Guidance for negotiating and implementing SLAs with ICT providers, including considerations for risk assessment, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring of service levels.
Emphasizes the critical role of SLAs in managing relationships with ICT providers, ensuring service quality, and maintaining operational resilience in compliance with DORA regulations.
By establishing comprehensive "Service Level Agreements with ICT Providers," financial entities can secure a commitment to high-quality ICT services, directly supporting their operational resilience objectives as mandated by DORA.
The "Service Provider Monitoring Procedures" document outlines the systematic approach financial entities must adopt to monitor and review the performance and risk management practices of their ICT service providers. This process is critical for ensuring that service delivery aligns with the operational resilience objectives mandated by the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The procedures apply to all external ICT service providers engaged by the financial entity, covering a wide range of services from cloud computing and data processing to cybersecurity defenses and infrastructure management. The scope includes continuous monitoring, periodic reviews, and incident-based assessments.
Strategies for implementing the monitoring procedures within the entity’s operational framework, including roles and responsibilities, resource allocation, and communication channels.
Emphasizes the importance of effective and systematic monitoring of ICT service providers as a critical component of operational resilience, in compliance with DORA's requirements.
By adopting the "Service Provider Monitoring Procedures," financial entities can ensure robust oversight of their ICT service providers, thereby supporting their overall operational resilience and compliance with DORA regulations.
In the evolving landscape of digital operations, cybersecurity information sharing has emerged as a pivotal component for enhancing the collective resilience of the financial sector. The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) recognizes the importance of establishing robust channels for sharing cybersecurity-related information among financial entities, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders. This chapter introduces the foundational principles and objectives that guide cybersecurity information sharing practices under DORA, emphasizing the role of collaboration in preempting, mitigating, and responding to cyber threats effectively.
The primary objectives of cybersecurity information sharing under DORA include:
This introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the mechanisms, protocols, and best practices that underpin effective cybersecurity information sharing within the framework of DORA. By adhering to these guidelines, financial entities can contribute to a more secure and resilient digital operational environment, safeguarding not only their operations but also the broader financial system from cyber threats.
Join the MISP community to leverage the collective knowledge and data on cybersecurity threats.
Integrate MISP within your cybersecurity infrastructure to facilitate the sharing and receiving of threat intelligence.
Collaborate with the financial sector-specific information sharing community through platforms like MISP Financial Sector.
The "Cybersecurity Information Sharing Policy Document" serves as a cornerstone for establishing a structured and secure framework for sharing cybersecurity-related information within the financial sector. This policy document is crafted to align with the principles and mandates of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), aiming to enhance the collective cybersecurity posture of financial entities through effective collaboration and information exchange.
This policy document outlines the objectives for cybersecurity information sharing, including:
The document specifies the types of information to be shared, which may include threat intelligence, vulnerability disclosures, incident reports, and best practices for cybersecurity risk management.
Detailed guidelines for participation, including eligibility criteria for entities wishing to join the information-sharing framework, responsibilities of participants, and the process for onboarding new members.
Measures to ensure the protection of sensitive information and the confidentiality of shared data, in line with data protection laws and regulations.
Clear definition of roles and responsibilities for all parties involved in the information-sharing process, including the designation of a central coordinating body.
Framework for the implementation and governance of the information-sharing policy, including mechanisms for monitoring compliance, resolving disputes, and updating the policy as needed.
This "Cybersecurity Information Sharing Policy Document" empowers financial entities to engage in proactive and collaborative efforts to combat cyber threats, significantly contributing to the resilience and stability of the financial ecosystem in accordance with DORA's objectives.
The "MISP Integration Plan" is designed to facilitate the structured integration of the Malware Information Sharing Platform & Threat Sharing (MISP) into the financial entity's cybersecurity framework. This plan aims to enhance the entity's capability to share, receive, and analyze cybersecurity threat information efficiently, in alignment with the objectives of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The scope of this plan includes the technical integration of MISP, training of personnel on its use, and the establishment of processes for sharing and managing cybersecurity information within the MISP platform.
A phased timeline for the implementation of the MISP integration plan, outlining key milestones, responsibilities, and expected completion dates.
Strategies for monitoring the effectiveness of MISP integration and its impact on the financial entity's cybersecurity posture, with provisions for periodic evaluation and adjustments to the plan as necessary.
By implementing the "MISP Integration Plan," financial entities can significantly improve their cybersecurity information sharing capabilities, fostering a proactive approach to threat intelligence and enhancing operational resilience in compliance with DORA.
The "Financial Sector Collaboration Agreements" document aims to formalize partnerships and collaborative efforts among financial entities for sharing cybersecurity information and best practices. This initiative is designed to enhance the collective resilience of the financial sector against cyber threats, in accordance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
The scope of these agreements includes the sharing of threat intelligence, vulnerability information, incident reports, and mitigation strategies among participating financial entities. The agreements outline the framework for collaboration, focusing on improving the detection, prevention, and response to cybersecurity threats within the sector.
Highlights the benefits of sector-wide collaboration, including enhanced threat intelligence, accelerated incident response times, and a unified approach to cybersecurity challenges.
By establishing "Financial Sector Collaboration Agreements," financial entities can create a robust network for cybersecurity information sharing, significantly strengthening the sector's resilience against cyber threats in line with DORA's objectives.
Actively share indicators of compromise (IoCs) and other cybersecurity threat information with peers.
Develop internal procedures for analyzing, processing, and disseminating threat intelligence from MISP.
Encourage a culture of openness and collaboration within the banking sector for proactive threat response.
The "Threat Intelligence Sharing Reports" are designed to provide comprehensive insights into current cybersecurity threats, vulnerabilities, and incidents relevant to the financial sector. This initiative, mandated under the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), aims to facilitate the exchange of timely and actionable threat intelligence among financial entities, enhancing the sector’s collective ability to preempt, mitigate, and respond to cyber threats effectively.
The reports cover a wide range of cybersecurity topics, including but not limited to malware trends, phishing campaigns, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and emerging vulnerabilities. They aim to encompass all relevant threat intelligence that could impact the operational resilience of financial entities.
Guidelines for the distribution of reports among participating entities, ensuring secure access to threat intelligence while maintaining confidentiality and data protection standards.
Procedures for entities to provide feedback on reports and contribute their own insights, fostering a collaborative approach to threat intelligence sharing.
By regularly producing and sharing "Threat Intelligence Sharing Reports," financial entities can significantly improve their cybersecurity posture and operational resilience, contributing to the security and stability of the broader financial system as envisioned by DORA.
The "Internal Threat Intelligence Handling Procedures" document outlines the structured approach for managing and utilizing threat intelligence within a financial entity. These procedures aim to ensure that threat intelligence is effectively processed, analyzed, and acted upon to enhance the entity's cybersecurity posture, in line with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
This document covers the entire lifecycle of threat intelligence within the organization, including collection, processing, dissemination, and storage of intelligence. It applies to all forms of threat intelligence, whether obtained from external sources, shared through industry collaborations, or generated internally.
Definition of roles and responsibilities for staff involved in threat intelligence handling, including training requirements to ensure competence and compliance with these procedures.
Measures to ensure compliance with legal, regulatory, and policy requirements related to threat intelligence handling, including provisions for regular audits and reviews of the procedures.
By establishing "Internal Threat Intelligence Handling Procedures," financial entities can maximize the value of threat intelligence, enhancing their ability to anticipate, respond to, and mitigate cyber threats in accordance with DORA's guidelines for operational resilience.
The objective of "Cybersecurity Collaboration Workshops and Training Sessions" is to foster a culture of knowledge sharing and collective defense within the financial sector against cyber threats. These initiatives, recommended under the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), aim to equip financial entities and their personnel with the latest cybersecurity practices, threat intelligence insights, and collaborative strategies for enhancing sector-wide resilience.
The scope of these workshops and training sessions includes the dissemination of current cyber threat landscapes, sharing of best practices in threat detection and response, and the development of collaborative strategies for threat intelligence sharing among financial entities.
Guidelines for financial entities on how to participate in these workshops and training sessions, including registration processes, prerequisites, and access to training materials.
Expected outcomes include enhanced cybersecurity awareness among financial entities, improved readiness to tackle cyber threats, and strengthened networks for collaborative defense within the financial sector.
By participating in "Cybersecurity Collaboration Workshops and Training Sessions," financial entities can significantly enhance their cybersecurity capabilities and contribute to the resilience and stability of the financial ecosystem, in line with the objectives of DORA.
Use shared threat intelligence to enhance your organization's cyber defense mechanisms.
Contribute to and utilize sector-wide best practices for cybersecurity as developed through collective intelligence.
Regularly review and update cyber resilience strategies to reflect the evolving threat landscape.
Collaboration with regulatory authorities for effective collective defense.
Active participation in information sharing networks to stay informed of the latest threats and trends.
The "Cyber Defense Enhancement Report" aims to document and assess the efforts and initiatives undertaken by financial entities to bolster their cyber defense capabilities. This report supports the overarching goal of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) to enhance sector-wide cyber resilience, providing insights into progress made, challenges encountered, and opportunities for further enhancements in cyber defense strategies.
This report covers a comprehensive analysis of cyber defense mechanisms, including technological solutions, procedural updates, employee training programs, and collaboration efforts within the financial sector. It aims to highlight the advancements made in protecting against, detecting, and responding to cyber threats.
Explanation of the methodology used to gather data, assess cyber defense enhancements, and develop the report, including tools, surveys, interviews, and analysis techniques.
Concluding remarks emphasizing the importance of ongoing efforts to enhance cyber defense capabilities and the critical role of collaboration and information sharing in achieving sector-wide cyber resilience.
Through the "Cyber Defense Enhancement Report," financial entities can benchmark their progress, identify areas for improvement, and contribute to a stronger, more resilient financial sector, in line with the principles of DORA.
The "Cyber Defense Enhancement Report" aims to document and assess the efforts and initiatives undertaken by financial entities to bolster their cyber defense capabilities. This report supports the overarching goal of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) to enhance sector-wide cyber resilience, providing insights into progress made, challenges encountered, and opportunities for further enhancements in cyber defense strategies.
This report covers a comprehensive analysis of cyber defense mechanisms, including technological solutions, procedural updates, employee training programs, and collaboration efforts within the financial sector. It aims to highlight the advancements made in protecting against, detecting, and responding to cyber threats.
Explanation of the methodology used to gather data, assess cyber defense enhancements, and develop the report, including tools, surveys, interviews, and analysis techniques.
Concluding remarks emphasizing the importance of ongoing efforts to enhance cyber defense capabilities and the critical role of collaboration and information sharing in achieving sector-wide cyber resilience.
Through the "Cyber Defense Enhancement Report," financial entities can benchmark their progress, identify areas for improvement, and contribute to a stronger, more resilient financial sector, in line with the principles of DORA.
The "Updated Cyber Resilience Strategies" document aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the revised strategies and practices adopted by financial entities to bolster their cybersecurity and operational resilience. This update, in line with the mandates of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), reflects the evolving cyber threat landscape and the need for continuous enhancement of cyber defenses within the financial sector.
The scope of these strategies includes the identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery from cyber incidents. It encompasses technological solutions, procedural guidelines, personnel training, and collaboration efforts both within and across entities in the financial sector.
A detailed plan outlining the steps for implementing the updated cyber resilience strategies, including timelines, responsibilities, and resource allocation.
Procedures for the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of the updated strategies, ensuring adaptability to the evolving cyber threat landscape.
By adopting the "Updated Cyber Resilience Strategies," financial entities can ensure a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity, significantly enhancing their resilience in the face of cyber threats in accordance with the principles of DORA.
For more information or inquiries, please feel free to reach out to us. You can either fill out the form below or send us an email directly: